|





|
|
|
Third
Normal Form (3NF) |
|
Aim:
remove non-key attributes that are dependant on other non-key
attributes.
|
| 3NF
Rule 1: |
All
data must be in 2NF.
|
|
3NF Rule 2: |
Remove NON-KEY attributes from the master table, that are dependant
on other NON-KEY attributes. Form a new detail table,
giving it a suitable key. Retain a copy of this key, in the
originating table, to act as a table link.
|
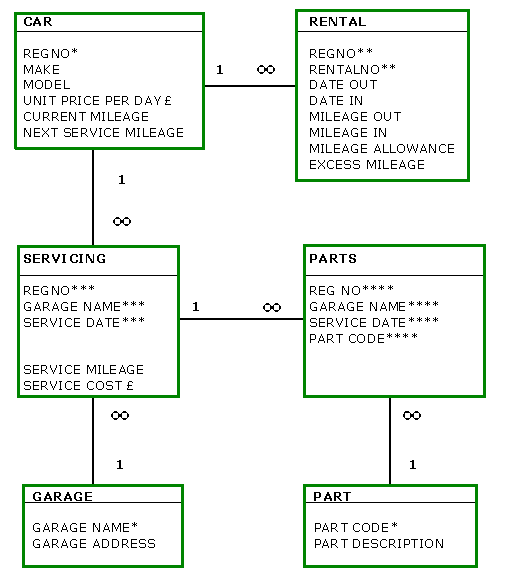
| Below
is the Second Normal Form model from the previous 2NF
page: |
|
|
|
As the data model is
in 2NF then it complies with Rule 1.
So now we need to examine each table to see if all the
attributes comply with the Rule 2. Lets start with the
CAR table.
As the CURRENT MILEAGE & NEXT SERVICE MILEAGE are
specific to the individual car; then they must depend
on the REGNO key. And hence are in 3NF already and can
therefore be discounted.
|
So that leaves the MAKE, MODEL & UNIT PRICE attributes:
is MAKE dependent on MODEL? Ask yourself this question;
if you know the MAKE, do you uniquely know the MODEL.
Well no, because 1 MAKE can have many MODELS. Just as
car manufacturers make many different models of car. However,
if you know the MODEL then you can uniquely identify
the MAKE. This means that MAKE is dependent on
MODEL and hence MAKE should be removed from the CAR table
and put in a new table. Does it seem logical then, to
make MODEL the key to this new table?
Yes, because by continually going back over the Normalisation
Rules we find an answer:
2NF Rule 2a states: Every non-key attribute
must be fully dependent on the
(entire) primary key.
So it is correct to create a new MODEL table and have
MAKE as an attribute &
have MODEL as the linking key to CAR.
The looking back over the previous Normalisation
Rules used, to find clues and hence answers to logical
questions is a fundamental concept. If you wish to Normalise
data correctly in industry - this must be done on as ongoing
process. During 2NF refer back to 1NF Rules; During 3NF
(as here) refer back to 3NF Rules etc.
So the remaining non-key attribute
in the CAR table is UNIT PRICE PER DAY. Does this hire
charge apply to individual cars or to cars, grouped by
model? It would seem logical that Norm would charge the
same price for a hire car model, because; each model will
cost the same for Norm to buy and run & customers
will not expect to be charged more for a 2002 hire car,
just because it is newer than the 2001 one, even though
they are the same model and hence specification.
So here is another business
orientated question - constant feedback from a client
is an important consideration to database designers
& developers, just as it is for any IT developer.
Remember that a database is a business tool, not just
a load of interfaces and table code. As stated before;
if a database isn't usable, then it won't be used!
Back to the Normalisation: as UNIT PRICE PER DAY is
dependent on MODEL then it too should be added to the
new MODEL table as an attribute. Version one of the
3NF data model is shown below.
|
|
|
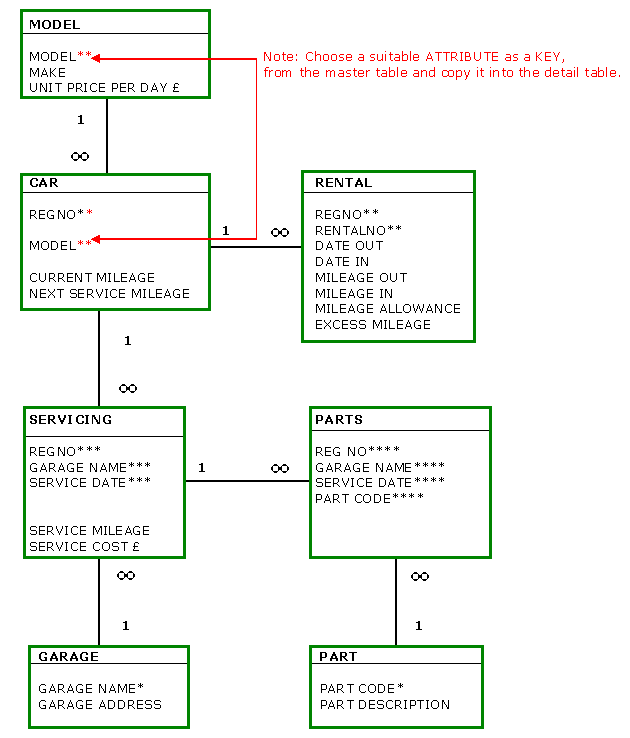
|
So
let us examine the remaining 5 tables: looking for non-key attributes
dependent on other non-key attributes.
Does SERVICING have any? No, because SERVICE MILEAGE & SERVICE
DATE are dependent on SERVICE DATE, which is a key attribute,
so the SERVICING table is in 3NF. As PARTS does not have any
non-key attributes; it too is in 3NF. Both GARAGE & PART
have non-key attributes, but they are both dependent on their
keys - this key dependency was part of the 2NF considerations.
That only leaves RENTAL to be transformed to 3NF and the Normalisation
of this data set is complete!
Look closely at RENTAL and then compare it with the previous
data model, you should see there is a part of the
data set missing! What about the customers?
As RENTAL had a detail table; CUST in the first Normalisation
example; this should now be joined to the MAINTENANCE data we
have been examining for the past few pages. The process of adding
previous tables from other Normalisation exercises is often
referred to as consolidation.
The consolidated data model
of the combined RENTALS and MAINTENANCE departments, for Norm's
Car Rentals is below.
|
|

|
| This
data set is now Normalised and it would be easy to implement;
using any relational database software package. |
| Next
follows some more detail about advanced Normalisation theory
and techniques for your information - |
| <<<Back
for Second Normal Form |
Next
for Other Normal Forms>>>
|
|
|
|
|
